Formula Sheet: Motion Equations at a Glance
Created by Shaleen Shekhar; Content Writer at The Physics Next
v = u + at
Final velocity (v) equals initial velocity (u) plus acceleration (a) times time (t).
s = ut + ½at²
Displacement (s) equals initial velocity (u) times time (t) plus half acceleration (a) times time squared.
v² = u² + 2as
Final velocity squared equals initial velocity squared plus twice acceleration times displacement.
s = vt - ½at²
Displacement equals final velocity times time minus half acceleration times time squared.
s = (u + v)/2 × t
Displacement equals average velocity (initial + final velocity divided by 2) times time.
a = (v - u) / t
Acceleration equals change in velocity divided by time.
s = ut + at²/2
Alternative form: Displacement equals initial velocity times time plus half acceleration times time squared.
v = s / t
Average velocity equals displacement divided by time.
t = (v - u) / a
Time taken equals change in velocity divided by acceleration.
s = vt - ½at²
Displacement equals final velocity times time minus half acceleration times time squared.


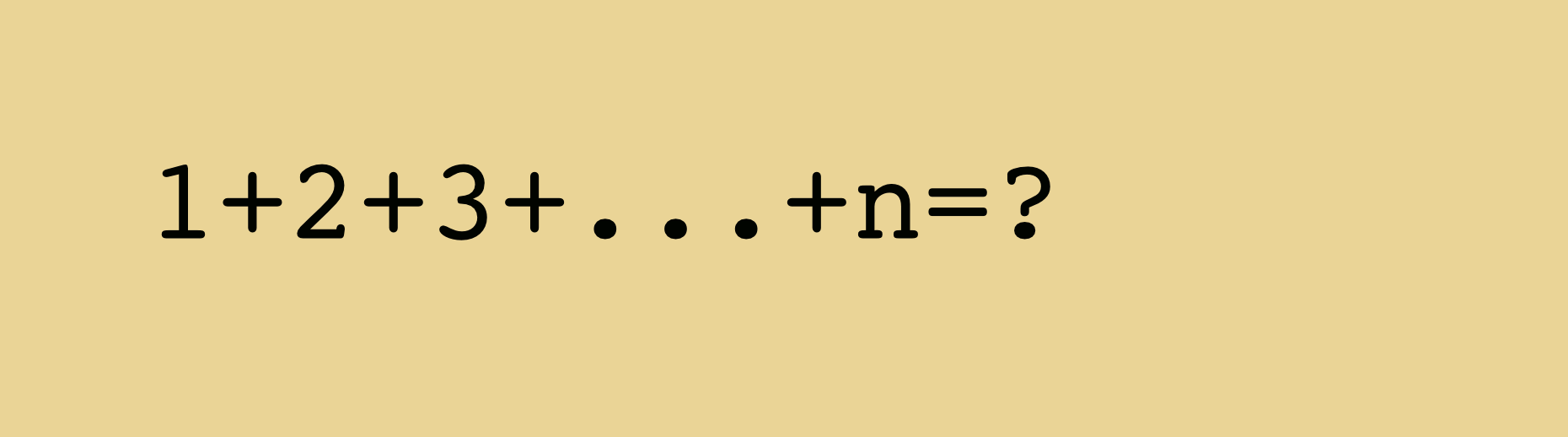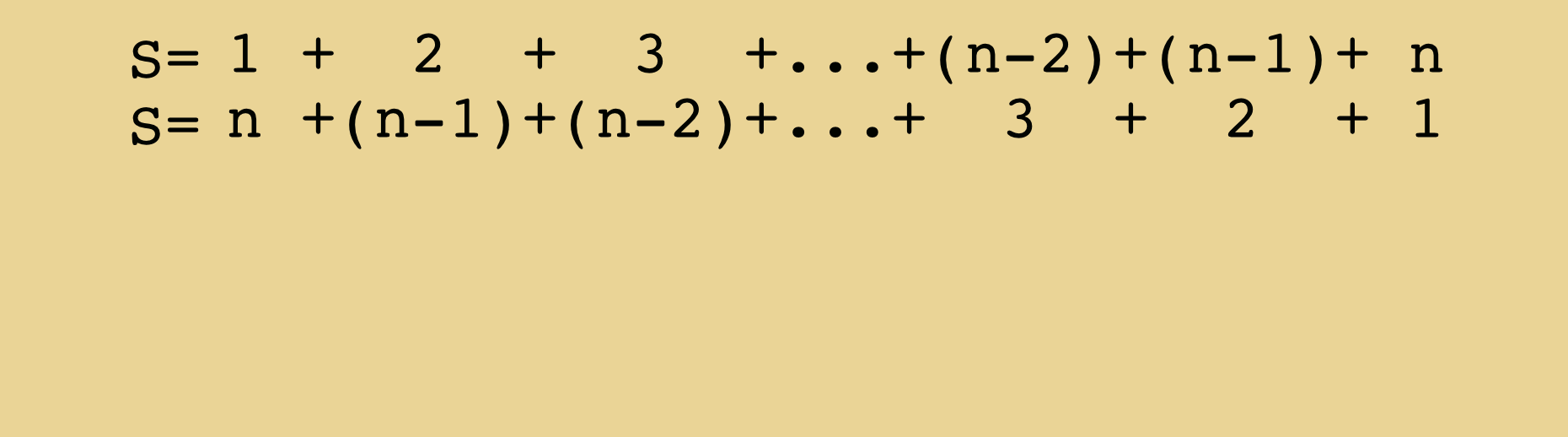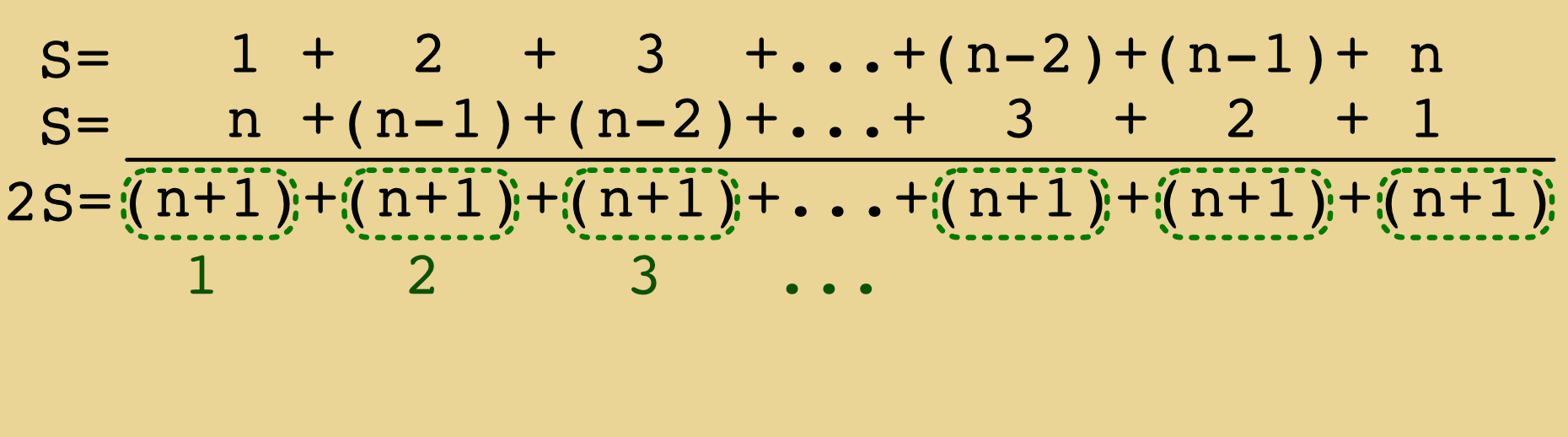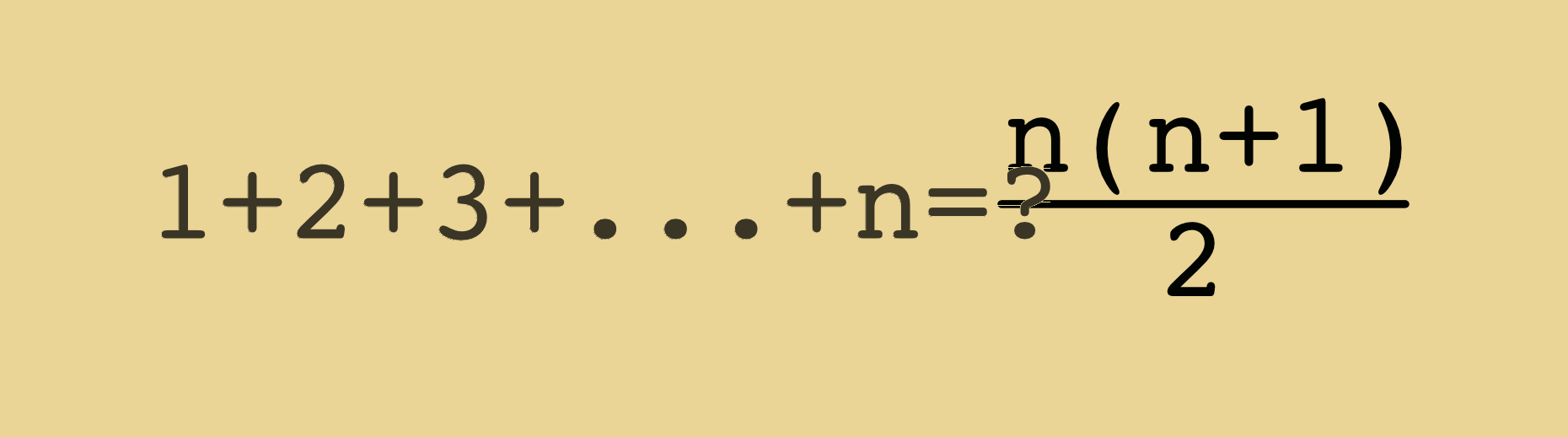


We will love to hear your thoughts — please share your comment on the blog post above!